A satellite project of labs.iximiuz.com - an indie learning platform to master Linux, Containers, and Kubernetes the hands-on way 🚀
Deep Dive: Exploring Docker "run" and "exec" Commands
|
According to StackOverflow's 2025 Developer Survey, there has never been a better time to learn how to use containers or become a Docker power user. For me, it's a perfect motivation booster to double down on the Docker Roadmap and bring you the best hands-on learning materials and the deepest possible technical dives. In today's issue, we'll explore what What does
|
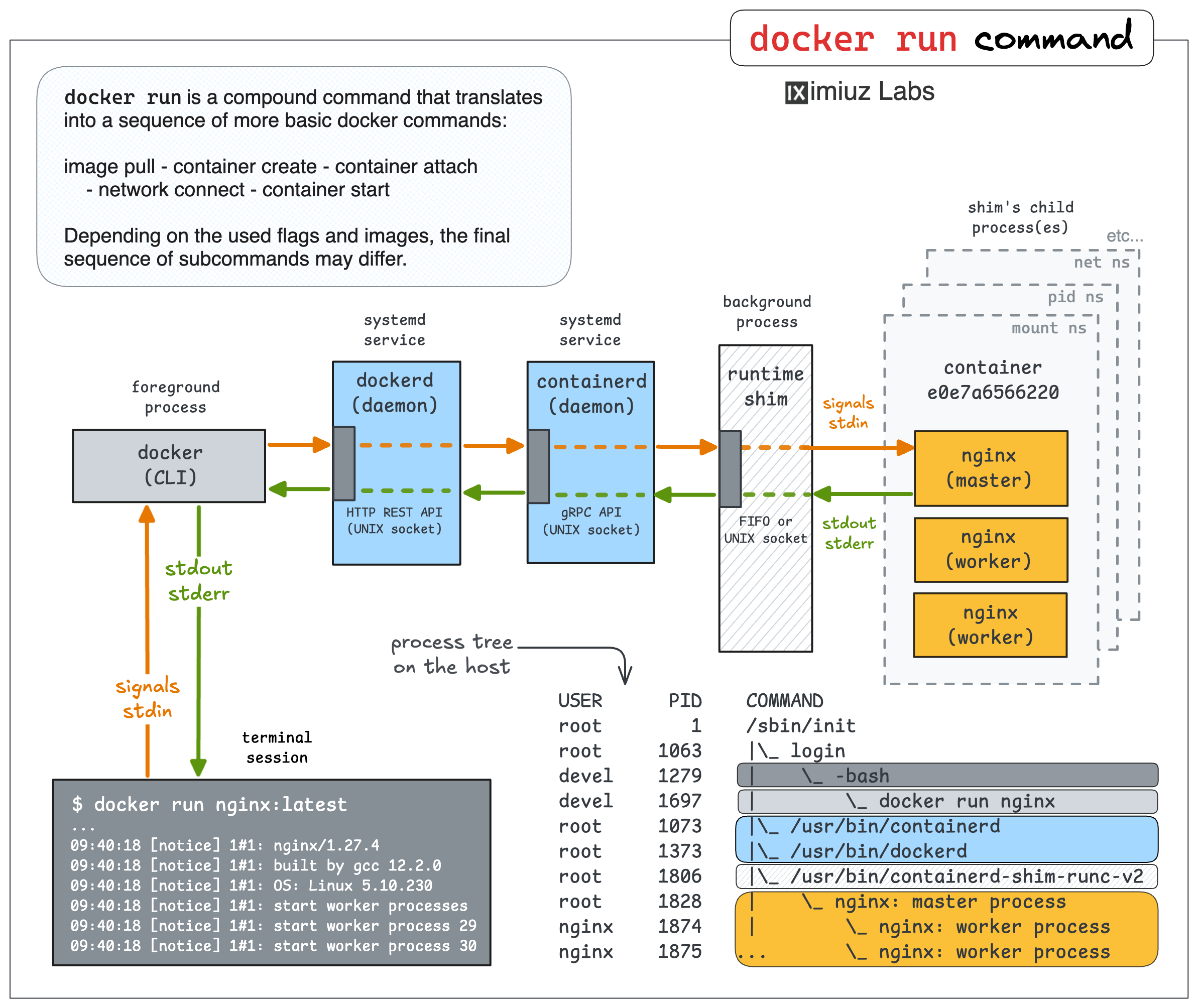 |
Tutorials and demos traditionally use the foreground form of the docker run command to keep things simple. However, most production applications you'll be dealing with will run in background containers. This is where the docker attach command comes in handy. It allows you to "reconnect" to the stdio streams of a container started in the background if the need arises.
The container runtime shim component on the above diagram acts as a server. It provides RPC means (e.g., a UNIX socket) to connect to it. And when you do so, it starts streaming the container's stdout and stderr back to your end of the socket. It can also read from this socket and forward data to the container's stdin. Hence, you re-attach to the container's stdio streams.
Thus, if you start a background container using the docker run command with the -d|--detach flag, you can reattach to its stdio streams later using docker attach
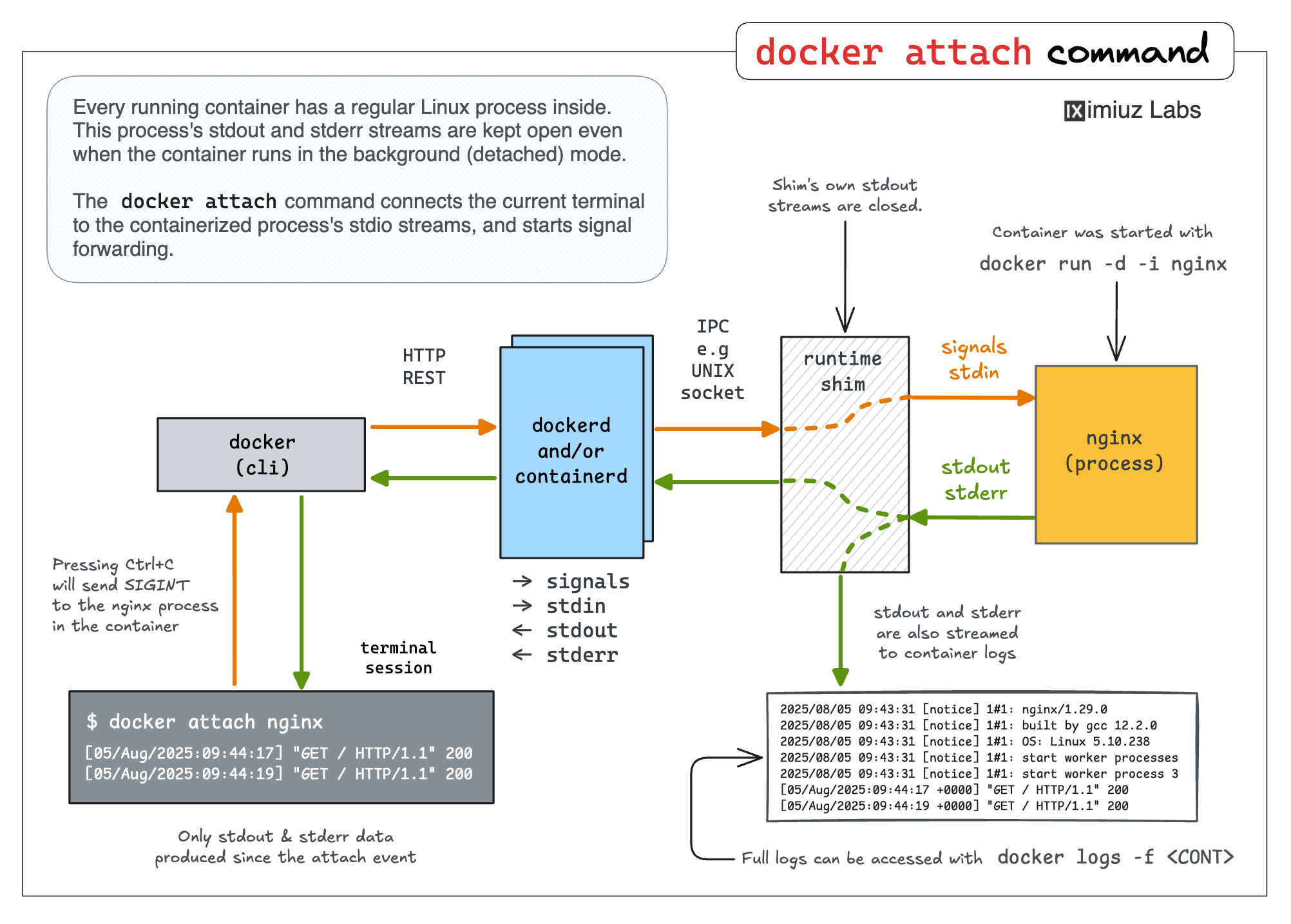 |
What about the docker exec command?
The docker exec command is frequently used in troubleshooting and debugging scenarios, when you need to execute a command or start an interactive shell inside of an already running container.
The exec command may resemble the attach command because you're targeting an existing container. However, in the case of attach, we were merely connecting our terminal to the containerized application's stdio streams (and starting to forward signals), while the exec command rather starts a new container, but kinda sorta inside of the existing one.
In other words, exec is a form of the run command 🤯
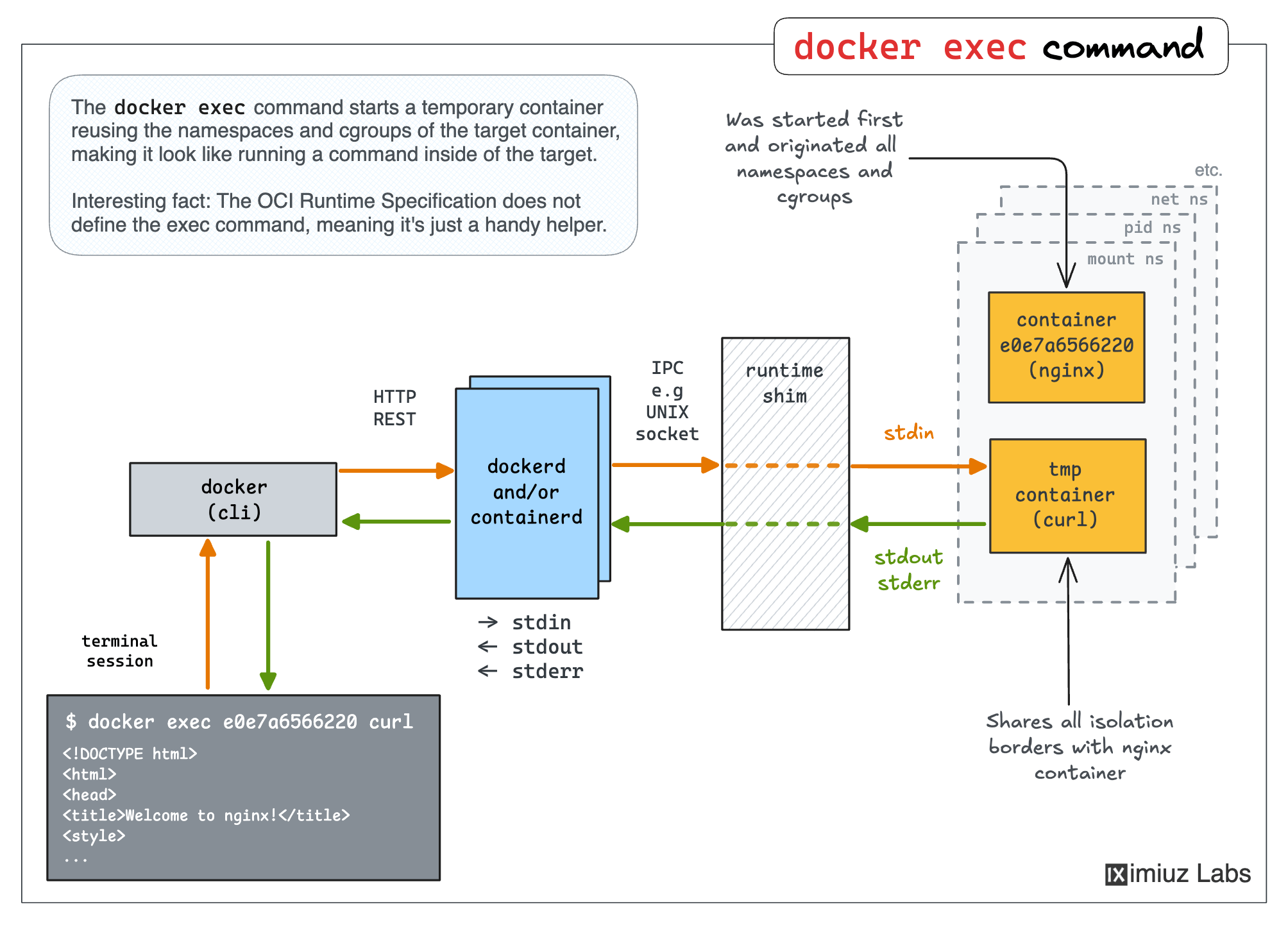 |
The trick here is that the auxiliary container created by the exec command shares all the isolation boundaries of the target container. I.e., the same net, pid, mount, etc. namespaces, same cgroups hierarchy, etc. So, from the outside, it feels like running a command inside an existing container.
How do other container runtimes implement the run and exec commands?
The above diagrams show the internals of the Docker implementation, but other container managers, such as containerd or nerdctl, behave similarly when it comes to run and exec commands.
Podman is probably the most prominent example of a daemonless container manager. However, even Podman employs container runtime shims. There is just one less hop in the relay when you attach to a Podman container.
An interesting specimen is Kubernetes. Kubernetes doesn't manage containers directly. Instead, every cluster node has a local agent, called kubelet, that in turn expects a CRI-compatible container runtime to be present on the node. However, on the lowest level, there are still the same shims and processes:
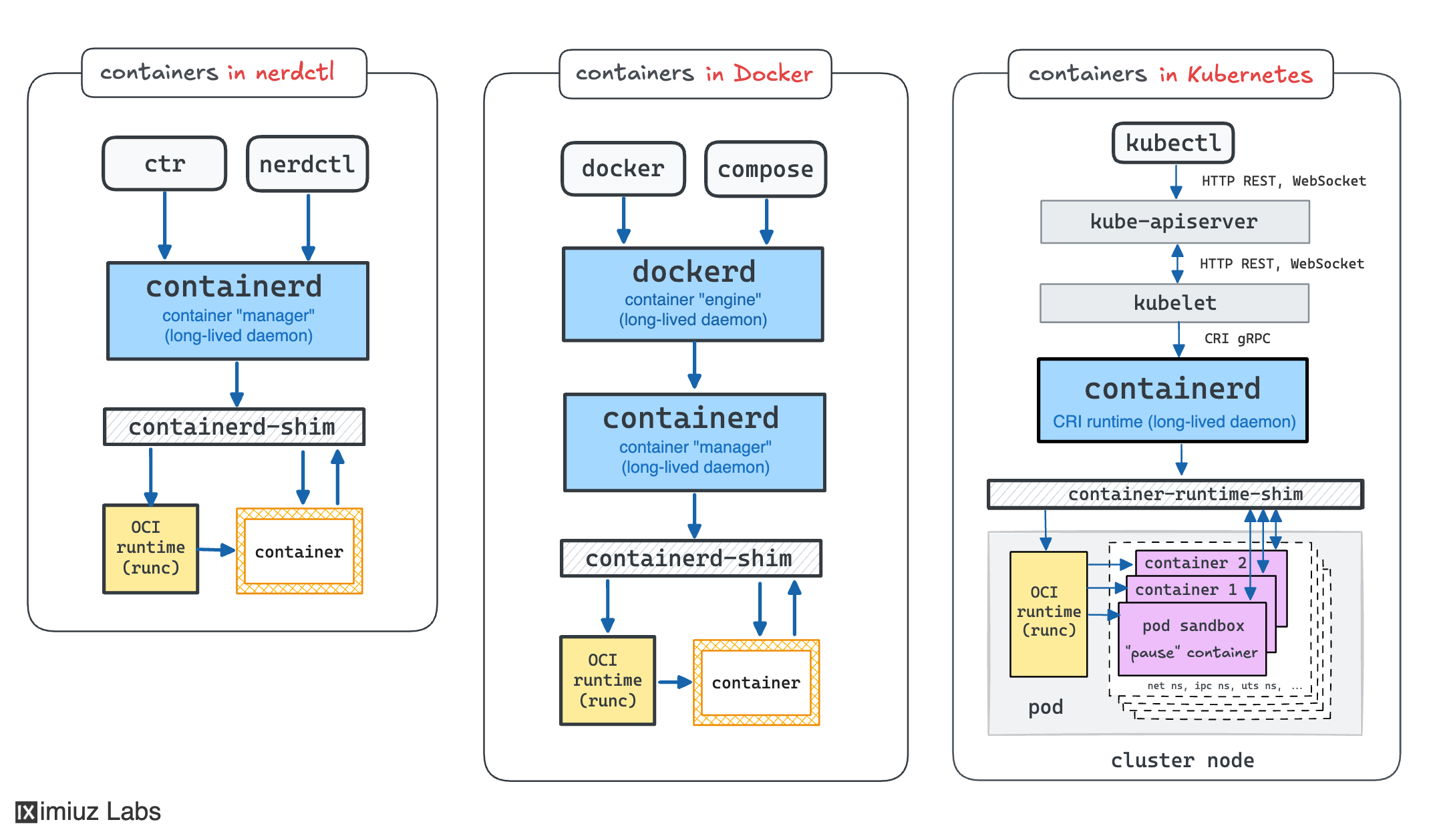 |
Similar to Docker, Kubernetes' command-line client, kubectl, also provides run, exec, and attach commands with an almost identical UX. The difference is that kubectl calls the central Kubernetes API server (instead of going straight to the container runtime or the corresponding kubelet on the target node), and asks it to create a pod, not a container. But luckily, pods are just groups of semi-fused containers, and having the API server on the way only adds an extra hop to the relay sequence, so conceptually, everything we learned so far is applicable to Kubernetes, too.
Read more and practice
You can find even more technical details on the docker run and docker exec commands, learn where the docker attach command may be a better tool for the job, and how is it different from the docker logs command in the most recent iximiuz Labs tutorial:
Docker Run, Attach, and Exec: How They Work Under the Hood (and Why It Matters)
Traditionally, the tutorial is packed with hands-on exercises that allow you to practice running containers, examining their logs, attaching to and executing commands in realistic yet controlled scenarios.
Happy containerizing! 🐳
P.S. This month has started rather well, and I couldn't be happier with the level of support I'm getting! Thank you!
Ivan on the Server Side
A satellite project of labs.iximiuz.com - an indie learning platform to master Linux, Containers, and Kubernetes the hands-on way 🚀